18+ Structure Of The Plant
There must be an area of growth similar to how the bones in your fingers arms and legs grow longer. Web - BBC Bitesize KS2 What is a plant.

Tropicanna Poison Grow Report Herbies Herbies
Part of Science Plants Take a closer look at the structure of plants.

. Plant cells like animal cells are eukaryotic meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Take up water and. Web Plant AnatomyPlant anatomy is the study of the shape structure and size of plants.
The term anatomy as applied to plants generally deals with structures that are observed under a high-powered light microscope or electron microscope. Web Introduction and Summary The parts of the plant are divided into two basic sections the root and the shoot. Web Stem Anatomy The stem and other plant organs are primarily made from three simple cell types.
These tissues transport water and other nutrients throughout the plant. Web Plant tissue systems fall into one of two general types. The cell wall is located outside the cell membrane.
Web There are three different types of root structure. Getting to Know Plants. The different parts of a plant have different functions.
The root the stem and the leaf as well as a set of reproductive parts that include. Cells of the meristematic tissue are found in meristems which are plant regions of continuous cell division and growth. Like other multicellular organisms plants grow through a combination of cell growth and cell division.
Web A flower sometimes known as a bloomor blossom is the reproductivestructure found in flowering plantsplants of the division Angiospermae. All plants have similar parts and each of these has a different job. Web The structure and functioning of plants even that of massive 100-metre tall trees is dependent on the structure of and processes occurring in microscopic cells.
Web A plant has many parts. Web The plant genome is organized into chromosomes that provide the structure for the genetic linkage groups and allow faithful replication transcription and transmission of the hereditary information. Flowers produce gametophytes which in flowering plants consist of a few haploid cells which produce gametes.
Different parts perform different functionalities. The root is comprised of all the structures below the soil and the shoot is composed of the structures above. There is and it is called the apical meristem which is shown here.
The parts of the plant body are also differentiated into two kinds of functional plant organs. The vegetative structures include the root stem and leaves. They are found in the stem the root the inside of.
The part of the plant that appears above the ground level is called the shoot system while the part of the plant which lies underneath the soil is called the root system. However these plants can be categorized into vascular plants and non-vascular plants. 3 The style is the thin stalk that connects the stigma down to the ovary.
In this book we look at the major organelles in cells the range of cell types in plants and how they are combined into tissues to create functioning leaves and other organs. There is a large variety of plants with different sets of structures. The roots also keep the plant steady.
The male gametophyte which produces non-motile sperm is enclosed within pollen grains. Plant Cell Definition Plant cells are eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that. Plants cells are complex structures with several organelles lacking in animal cells.
Web Plant Structure - The Parts of a Plant and Flower 1 The stigma is the sticky tip where pollen grains stick. Web plant cell the basic unit of all plants. There are three main tissue types called epidermal ground and vascular tissue.
Genome sizes in plants are remarkably diverse with a 2350-fold range from 63 to 149000 Mb divided into n2 to n approximately 600 chromosomes. When fertilized the ovules become the plants. Parenchyma cells are the most common plant cells.
The reproductive parts consist of the flower fruit and seed. Web By the definition used in this article plants form the clade Viridiplantae green plants which consists of the green algae and the embryophytes or land plants hornworts liverworts mosses lycophytes ferns conifers and. Web Figure 1.
Among these are the cell wall central vacuole and plastids the most familiar of which are chloroplasts. Plastids are membrane-bound. In a fibrous root system composed of many small roots no single root dominates.
It consists mainly of cellulose and may also contain lignin which. Web The parts of a plant and their jobs. The roots of a plant.
Web Plant Cell Structures The large central vacuole is surrounded by its own membrane and contains water and dissolved substances. Included in the shoot of seed plants are the stem the leaves and the seeds. Web This is a diagram of the anatomy of a plant with labels of structural parts of the plants and the roots.
Web Plant anatomy is the study of the tissue and cell structure of plant organs. A taproot characteristic of dicots is a single dominant root from which smaller secondary roots extend. Most plants continue to grow throughout their lives.
2 The ovary is at the base of the pistil and contains the ovules. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. Parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma cells.
Web Let us have a detailed look at the plant cell its structure and the functions of different plant cell organelles. Meristematic tissue and permanent or non-meristematic tissue. As a part of botany the study of plants plant anatomy focuses on the structural or body parts and systems that make up a plant.
Vascular plants have a system of special tissue called the xylem and phloem. Web plant kingdom Plantae any multicellular eukaryotic life-form characterized by 1 photosynthetic nutrition a characteristic possessed by all plants except some parasitic plants and underground orchids in which chemical energy is produced from water minerals and carbon dioxide with the aid of pigments and the radiant energy of. A typical plant body consists of three major vegetative organs.
Web The plant shoot system consists of the stem leaves and reproductive organs.
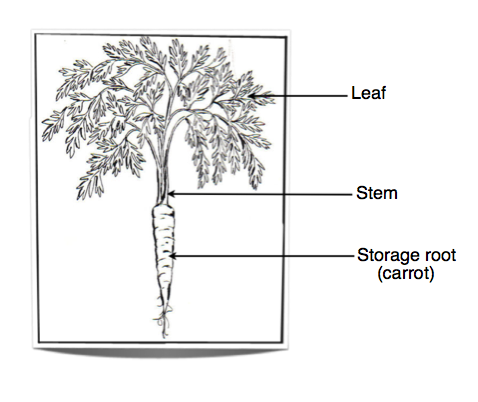
Ib Biology Notes 9 1 Plant Structure And Growth

Outdoor Wire Netted Plant Protector Dunelm

Set Review 10311 1 Orchid Botanicals 18 Bricks For Bricks
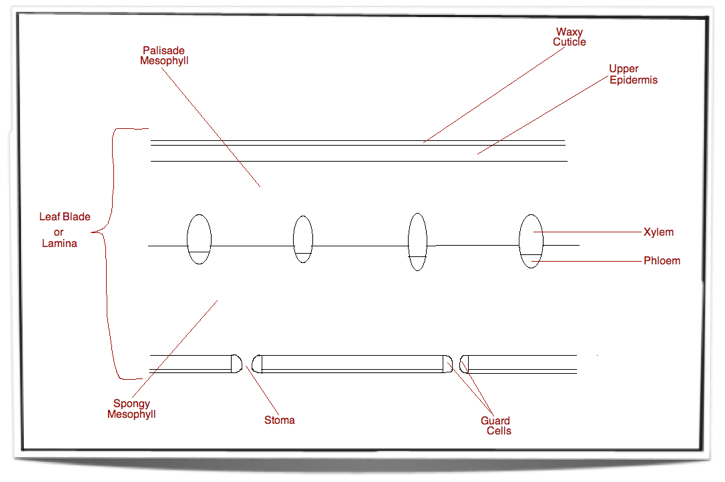
Ib Biology Notes 9 1 Plant Structure And Growth

Plant Structures Biology For Majors Ii
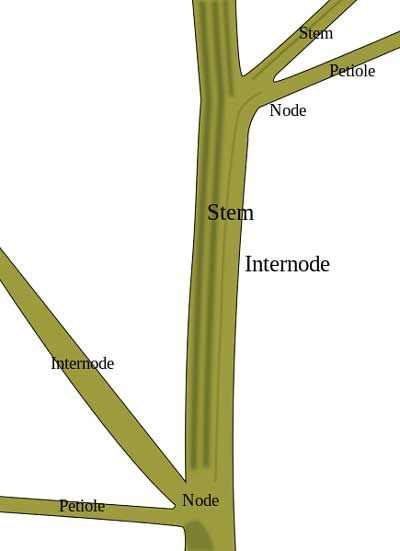
Plant Structure Parts Functions Facts Science4fun

Structure Of Life Interactive Notebook Pages Print Or Digital Inb Interactive Science Notebook Science Cells Homeschool Science

Cannabis Vegetative Stage How To Guide Dutch Passion

An Evergreen For Winter Structure Beauty Morning Ag Clips

Thompson And Morgan Hydrangea Cloud Nine 9cm Pot X 2 Inc Robert Dyas

Plant Structure Gidemy Class Notes

Learning Important Lessons From 2022 S Big Wet Groundcover

Cannabis Nodes What Are Weed Nodes And Why Are They Important Nuggmd

Wisteria Sinensis Blue Grafted 5 6ft Extra Large In A 5l Pot
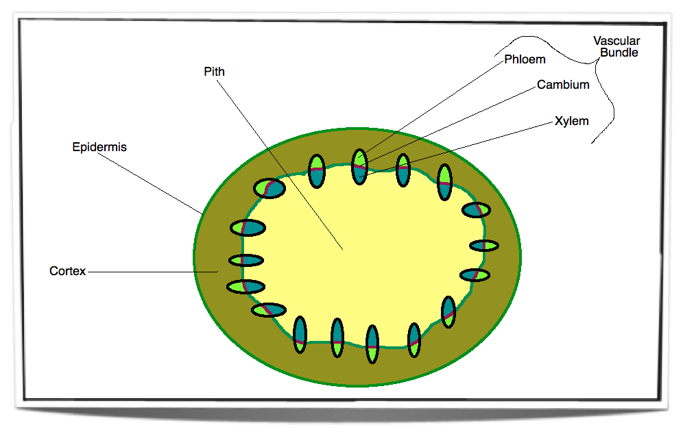
Ib Biology Notes 9 1 Plant Structure And Growth
Vascular Plants Vs Non Vascular Plants Definition 18 Differences Examples Phd Nest
Ferm Living Agnes Braided Rattan Plant Stand Dotmaison